A WELL-ESTABLISHED SAFETY PROFILE1
ESTABLISHED DDI PROFILE FOR PEOPLE WITH CHRONIC HEP C1,2
Only EPCLUSA has
No clinically significant drug interactions with1:
-
Ethinyl estradiol/norgestimate-based birth controla
aAmong first-line pangenotypic regimens.
EPCLUSA HAS NO INTERACTIONS
EXPECTED WITH2:
Antipsychotics
- ABILIFY (aripiprazole)
- SEROQUEL (quetiapine)
Opioids
- Fentanyl
- Oxycodone
Additional Information on EPCLUSA Drug Interactions1
Coadministration of EPCLUSA is not recommended with:
Antiarrhythmics
- Amiodarone, due to the risk of symptomatic bradycardia
P-gp inducers and/or moderate to strong inducers of CYP2B6, CYP2C8, or CYP3A4
- May significantly decrease plasma concentrations of sofosbuvir and/or velpatasvir, leading to reduced therapeutic effect of EPCLUSA
Certain other medications
-
Omeprazole/other PPIs, phenobarbital, phenytoin, rifabutin, rifapentine, efavirenz,
and tipranavir/ritonavir, due to decreased concentration of sofosbuvir and/or
velpatasvir
- If medically necessary, EPCLUSA should be administered with food and taken 4 hours before omeprazole 20 mg. Use with other PPIs has not been studied
Other considerations:
- Additional monitoring/dosing adjustments may be required with rosuvastatin or atorvastatin, as they may be associated with an increased risk of myopathy, including rhabdomyolysis
- Clearance of HCV infection with DAAs may alter hepatic function, impacting safe and effective use of concomitant medications. Frequent monitoring of relevant laboratory parameters and dose adjustments of certain concomitant medications may be necessary. See the EPCLUSA full Prescribing Information for a detailed list of additional drugs with no known interactions and other coadministration recommendations
MOST COMMON ADVERSE REACTIONS IN THE SIMPLIFY STUDY1
| Adverse Reactions | SIMPLIFY Study (n=103) |
|---|---|
| Fatigue | 18% |
| Nausea | 13% |
| Headache | 11% |
- The adverse reactions observed from SIMPLIFY both overall and in subjects on MOUD were consistent with the known safety profile of EPCLUSA
- Adverse reactions leading to permanent discontinuation of treatment were not observed in any subjects
DRUG INTERACTIONS1
Clearance of hepatitis C virus infection with direct-acting antivirals may lead to changes in hepatic function, which may impact safe and effective use of concomitant medications. Frequent monitoring of relevant laboratory parameters (eg, INR in patients taking warfarin and blood glucose levels in diabetic patients) and dose adjustments of certain concomitant medications may be necessary.
Potentially significant drug interactions: Alteration in dose or regimen may be recommended based on drug interaction studies or predicted interaction1,b
| Concomitant Drug Class | Effect on Concentrationc | Clinical Effect/Recommendation |
|---|---|---|
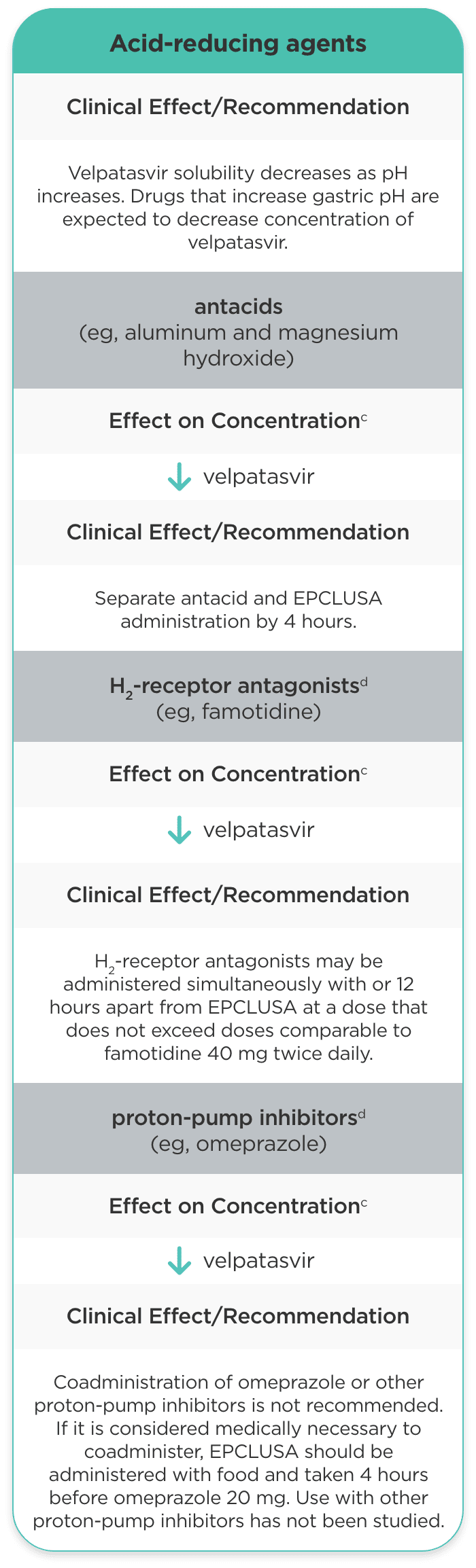
| Acid-reducing agents |
Velpatasvir solubility decreases as pH increases. Drugs that increase gastric pH are expected to decrease concentration of velpatasvir. |
|
|
antacids (eg, aluminum and magnesium hydroxide) |
velpatasvir |
Separate antacid and EPCLUSA administration by 4 hours. |
|
H2-receptor antagonistsd (eg, famotidine) |
velpatasvir |
H2-receptor antagonists may be administered simultaneously with or 12 hours apart from EPCLUSA at a dose that does not exceed doses comparable to famotidine 40 mg twice daily. |
|
proton-pump inhibitorsd (eg, omeprazole) |
velpatasvir |
Coadministration of omeprazole or other proton-pump inhibitors is not recommended. If it is considered medically necessary to coadminister, EPCLUSA should be administered with food and taken 4 hours before omeprazole 20 mg. Use with other proton-pump inhibitors has not been studied. |
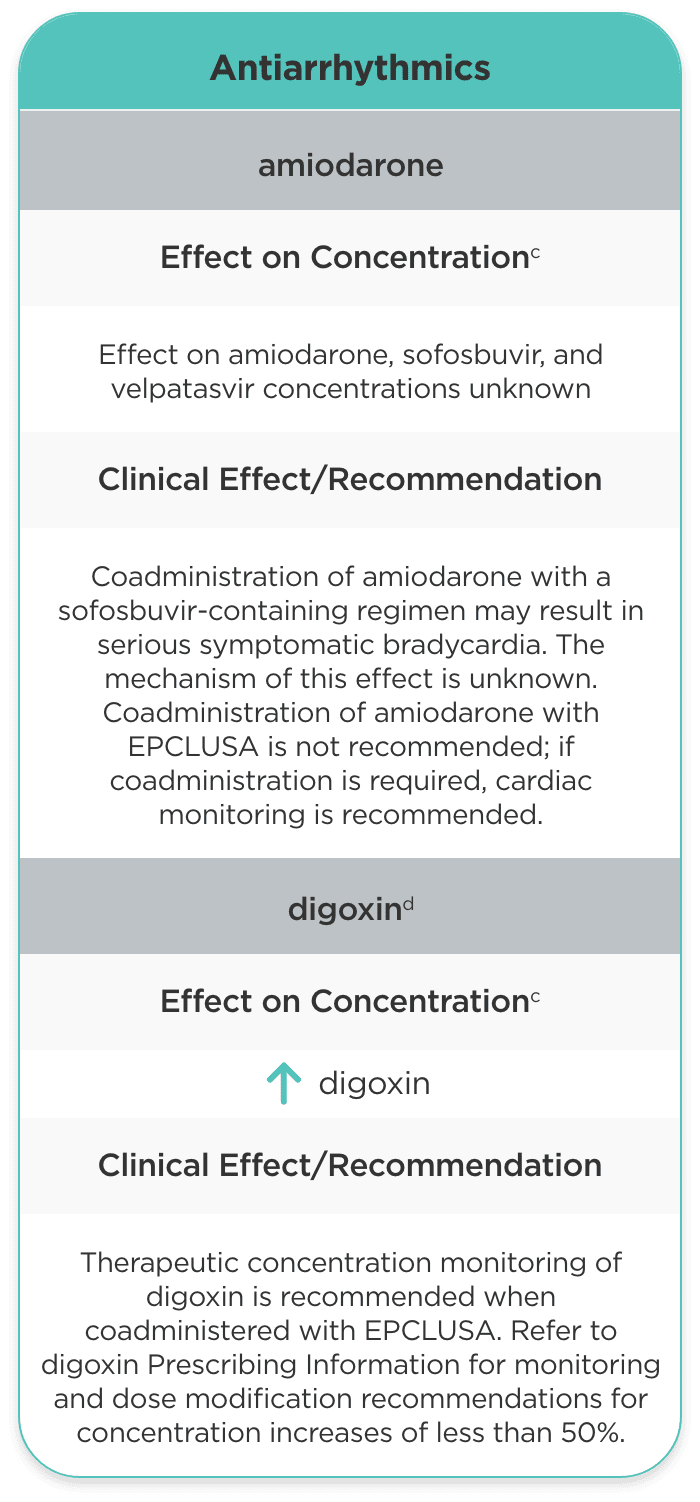
| Antiarrhythmics | ||
| amiodarone |
Effect on amiodarone, sofosbuvir, and velpatasvir concentrations unknown |
Coadministration of amiodarone with a sofosbuvir-containing regimen may result in serious symptomatic bradycardia. The mechanism of this effect is unknown. Coadministration of amiodarone with EPCLUSA is not recommended; if coadministration is required, cardiac monitoring is recommended. |
| digoxind |
digoxin |
Therapeutic concentration monitoring of digoxin is recommended when coadministered with EPCLUSA. Refer to digoxin Prescribing Information for monitoring and dose modification recommendations for concentration increases of less than 50%. |
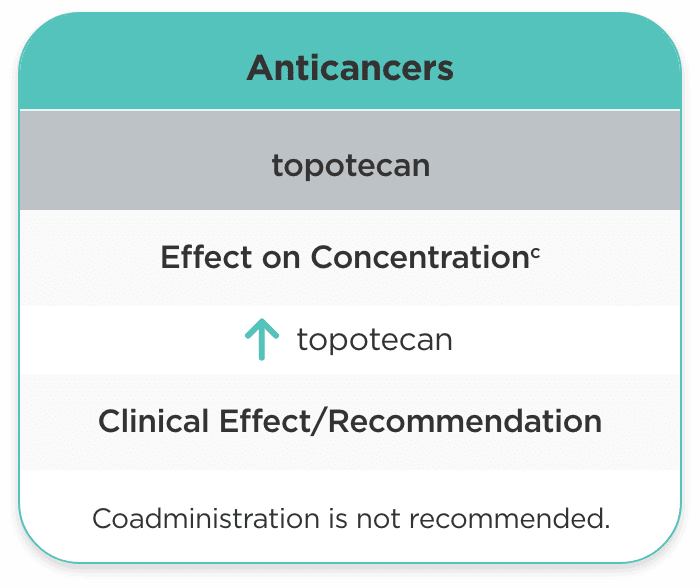
| Anticancers | ||
| topotecan |
topotecan |
Coadministration is not recommended. |
| Anticonvulsants | ||
| carbamazepined, phenytoin, phenobarbital |
sofosbuvir velpatasvir |
Coadministration is not recommended. |
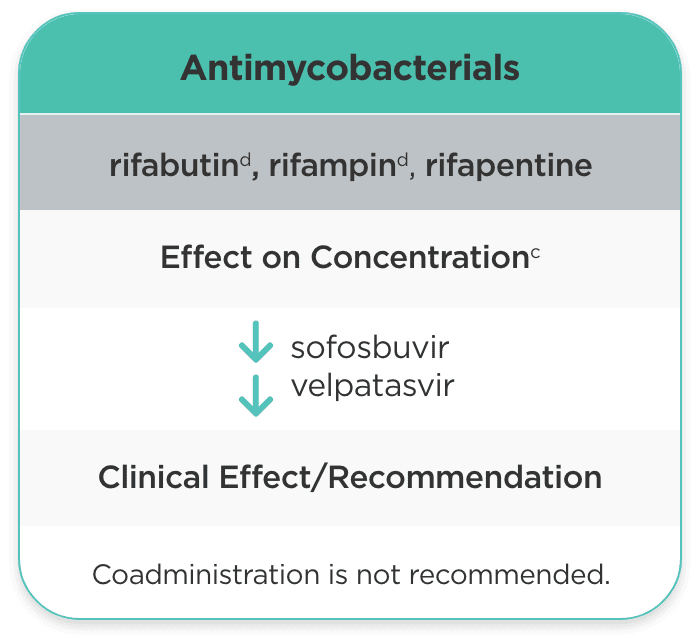
| Antimycobacterials | ||
| rifabutind, rifampind, rifapentine |
sofosbuvir velpatasvir |
Coadministration is not recommended. |
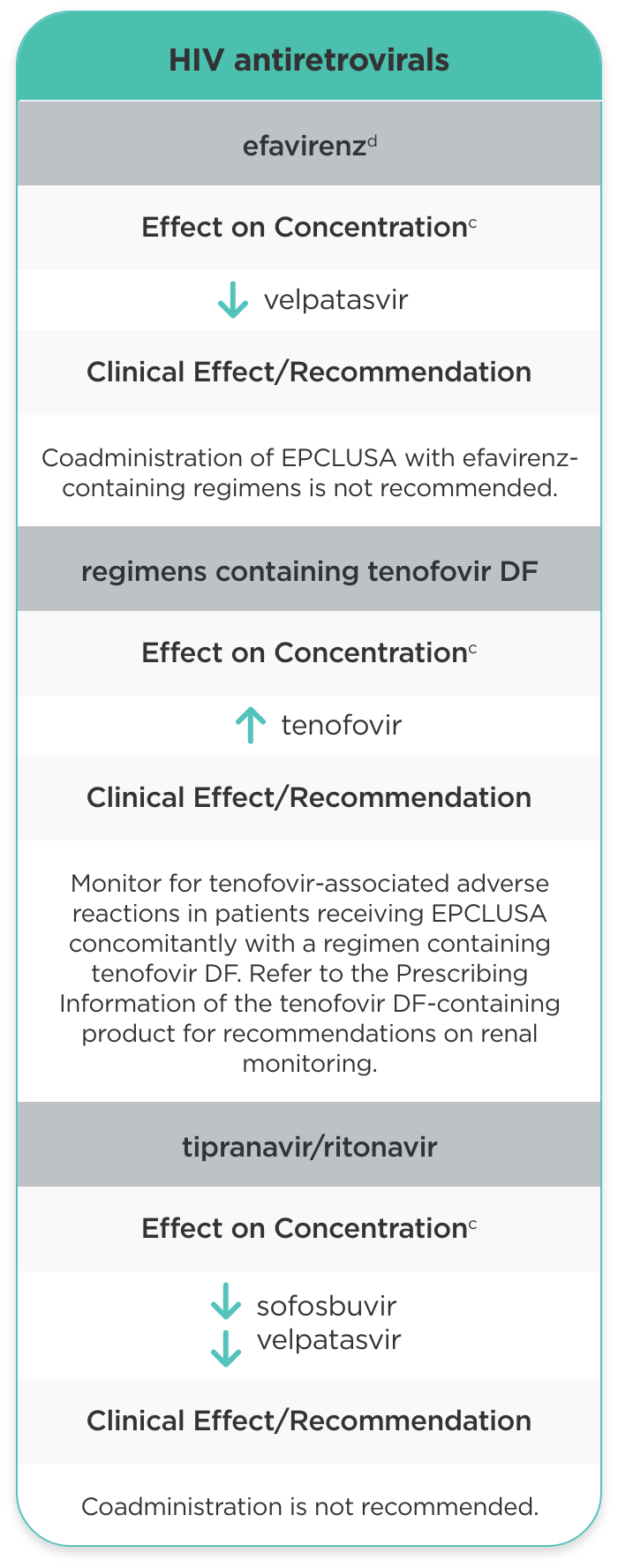
| HIV antiretrovirals | ||
| efavirenzd |
velpatasvir |
Coadministration of EPCLUSA with efavirenz-containing regimens is not recommended. |
| regimens containing tenofovir DF |
tenofovir |
Monitor for tenofovir-associated adverse reactions in patients receiving EPCLUSA concomitantly with a regimen containing tenofovir DF. Refer to the Prescribing Information of the tenofovir DF-containing product for recommendations on renal monitoring. |
| tipranavir/ritonavir |
sofosbuvir velpatasvir |
Coadministration is not recommended. |
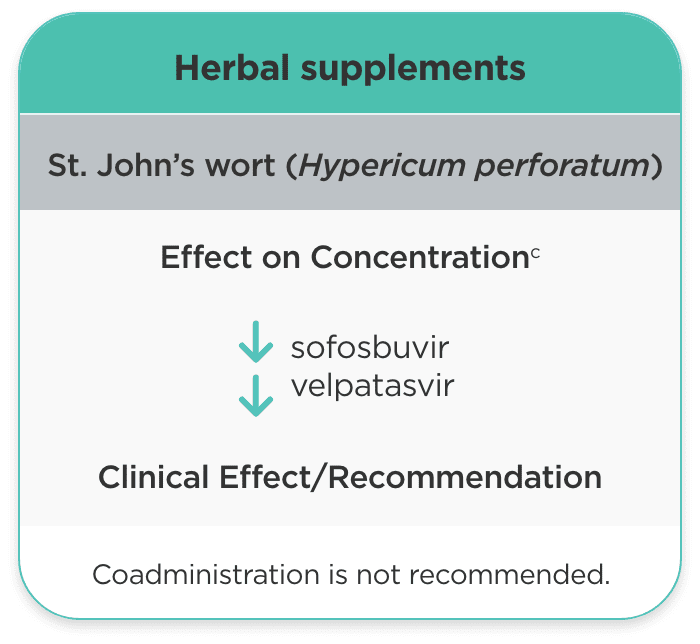
| Herbal supplements | ||
| St. John’s wort (Hypericum perforatum) |
sofosbuvir velpatasvir |
Coadministration is not recommended. |
| HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors | ||
| rosuvastatind |
rosuvastatin |
Coadministration of EPCLUSA with rosuvastatin may significantly increase the concentration of rosuvastatin, which is associated with increased risk of myopathy, including rhabdomyolysis. Rosuvastatin may be administered with EPCLUSA at a dose that does not exceed 10 mg. |
| atorvastatind |
atorvastatin |
Coadministration of EPCLUSA with atorvastatin may be associated with increased risk of myopathy, including rhabdomyolysis. Monitor closely for HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor-associated adverse reactions, such as myopathy and rhabdomyolysis. |

b This table is not all inclusive.1
c = decrease, = increase.1
d These interactions have been studied in healthy adults.1
- No clinically significant interactions between velpatasvir and pravastatin. Interactions between sofosbuvir and pravastatin have not been studied1
- No clinically significant interactions with MOUD such as buprenorphine/naloxone, methadone, or naltrexone1
Consult the full Prescribing Information for EPCLUSA (sofosbuvir/velpatasvir) for more information on potentially significant drug interactions, including clinical comments.
Please see the full Prescribing Information or Package Insert for EPCLUSA.
ADVERSE REACTIONS (ALL GRADES) REPORTED IN ≥5% OF SUBJECTS TREATED WITH EPCLUSA IN ASTRAL-11,3
ASTRAL-1 Study (12 weeks)1,3
| Adverse Reactions | EPCLUSA (n=624) | Placebo (n=116) |
|---|---|---|
| Headache | 22% | 28% |
| Fatigue | 15% | 20% |
| Nausea | 9% | 11% |
| Insomnia | 5% | 9% |
| Asthenia | 5% | 8% |
- The majority of these adverse reactions in ASTRAL‑1 were of mild severity (Grade 1, 79%)1
- The adverse reactions observed in subjects treated with EPCLUSA in ASTRAL‑2 and ASTRAL‑3 were consistent with those observed in ASTRAL‑11
- Irritability was also observed in ≥5% of subjects treated with EPCLUSA in ASTRAL‑31