INDICATION
EPCLUSA (sofosbuvir 400 mg/velpatasvir 100 mg, 200 mg/50 mg tablets; 200 mg/50 mg, 150 mg/37.5 mg oral pellets) is indicated for the treatment of patients 3 years of age and older with chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) genotype 1-6 infection without cirrhosis or with compensated cirrhosis and in combination with ribavirin for those with decompensated cirrhosis.
Please see below for Important Safety Information for EPCLUSA.
About HCV
Screen and treat to help manage chronic hepatitis C
Featured patient
compensated by Gilead.
~2.7 million Americans were living with CHRONIC HEPATITIS C INFECTION in 20181
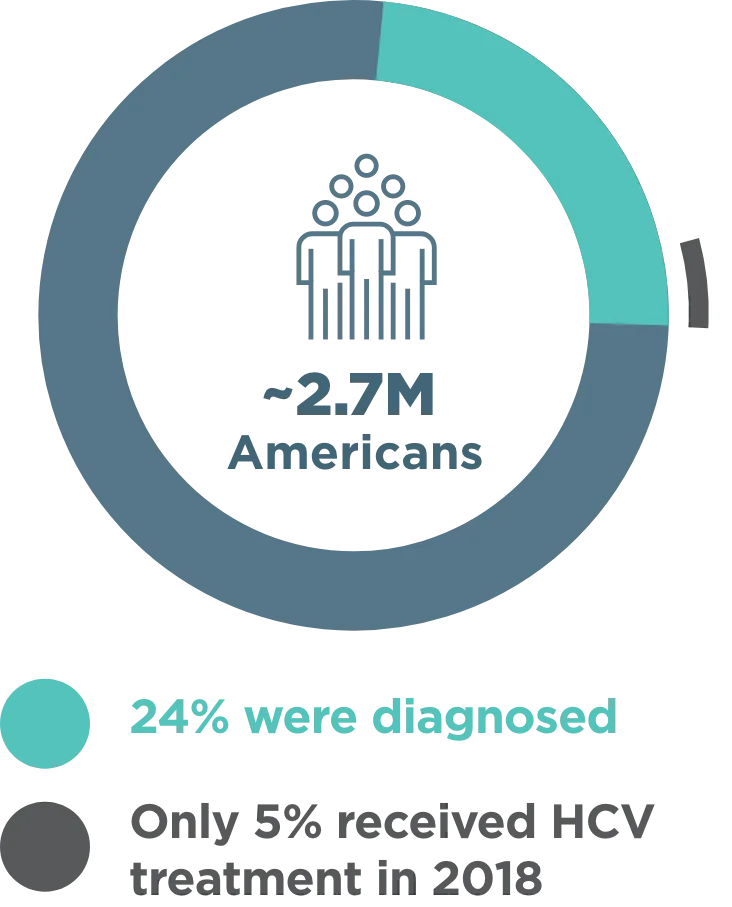
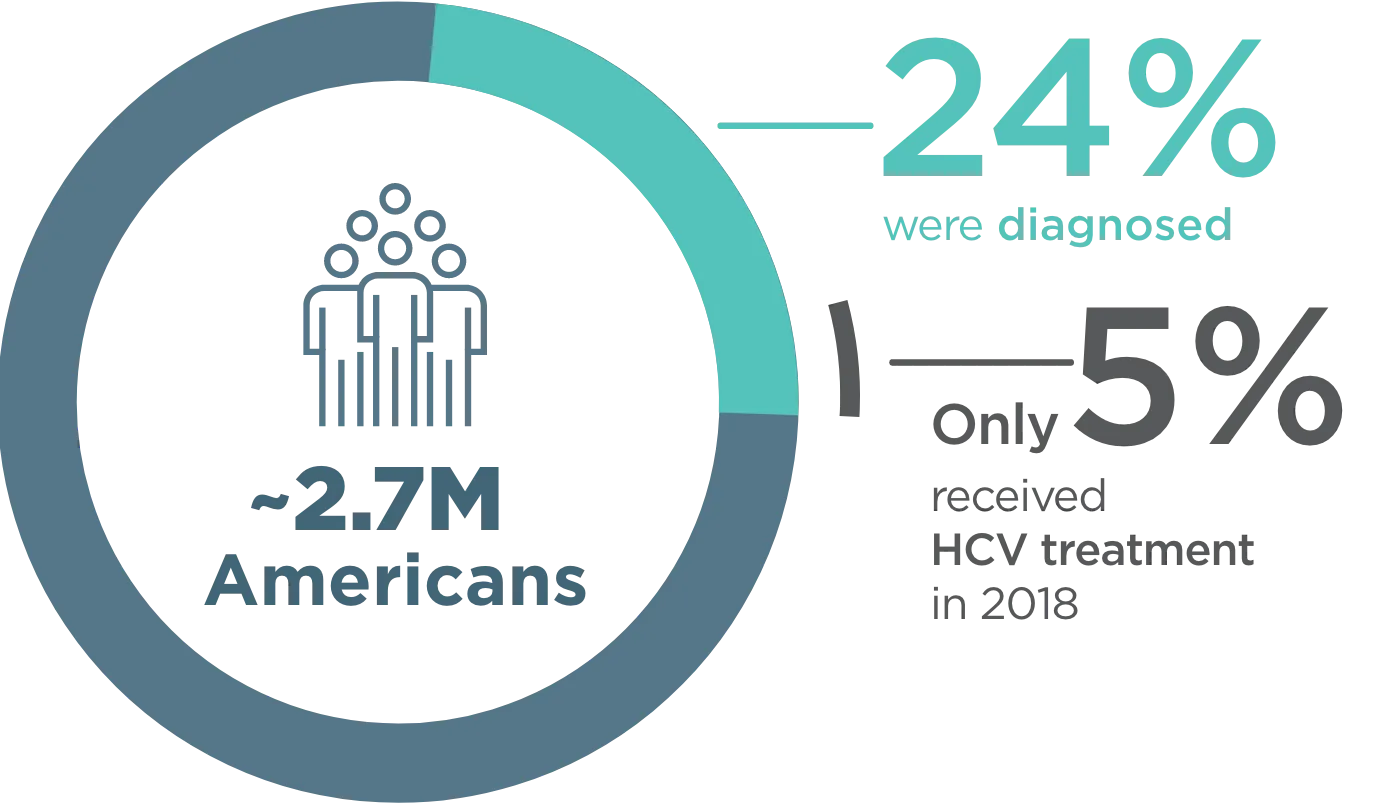
- Cases in the US more than doubled from 2012-2019 due to injection drug use2
- The most rapid increase was in adults aged 20-39 years who inject drugs3
Guidelines recommend universal testing and immediate treatment
|
Test all adult patients at least once3-5 |
Test
all at-risk patients3-8 |
Begin treating
all patients4,6 |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| AASLD/ |
|
|
|
| CDC |
|
|
|
| USPSTF |
|
|
|
| EASL |
|
|
|
| ASAM |
|
||
| ACOG |
|
a Unless they have limited life expectancy that cannot be remediated by HCV therapy.4
b Except in settings where the prevalence of HCV infection (HCV RNA-positivity) is <0.1%.5
c Recommendations for screening of adults (18-79 years).3
d Unless they have limited life expectancy due to non-liver-related comorbidities.6
e “At-risk” refers to patients with a history of drug use (current and past) and all persons living with HIV infection.7
f “At-risk” refers to pregnant individuals. ACOG recommends screening during each pregnancy and to begin HCV treatment postpartum and/or after completion of breastfeeding.8
Key Steps To Testing And Diagnosing HCV4
Run an HCV antibody test
Choose the lab's "reflex-testing" option at the testing step so that an HCV RNA test will be run automatically if the antibody test is positive.
Nonreactive HCV antibody test = STOPa
No virus detected

Reactive HCV antibody test
Positive result or reactive result confirms exposure to the virus. Run an HCV RNA test to verify.

Run an HCV RNA test
Run either a qualitative or quantitative RNA test. This will confirm the presence of the virus. Choose “reflex testing” option to automate this step.

RNA not detected = STOPa-c

RNA detected
Detection confirms presence of virus.
Diagnose current HCV infection.

Follow pre-treatment steps

INITIATE TREATMENT

HCV antibody test with reflex to quantitative HCV RNA test:
- CPT code - 86803
- Quest DiagnosticsTM code - 8472
- LabCorp code - 1441279,10
Reflex Testing: Diagnosis can be facilitated by automatically testing for HCV RNA on the same sample if the HCV antibody test is positive.
a For persons who might have been exposed to HCV within the previous 6 months, consider retesting for HCV antibodies or ordering an HCV RNA test. For persons who are immunocompromised, testing for HCV RNA can be considered.
b Repeat HCV RNA testing if the person tested is suspected to have had HCV exposure within the previous 6 months or has clinical evidence of HCV disease.
c Annual testing recommended for active injection drug users.
Cure = sustained virologic response (SVR12; HCV RNA <LLOQ 12 weeks after treatment completion).11
